This guide will help you get ready for your Whipple procedure at MSK. It will also help you know what to expect as you recover.
Use this guide as a source of information in the days leading up to your surgery. Bring it with you on the day of your surgery. You and your care team will use it as you learn more about your recovery.
About your Whipple procedure
The Whipple procedure is done to remove a tumor in the head of your pancreas, your ampulla, or the first part of your duodenum. These organs are located in the back of your abdomen (belly) behind your stomach and just above your small intestine (see Figure 1).
About your pancreas and surrounding organs
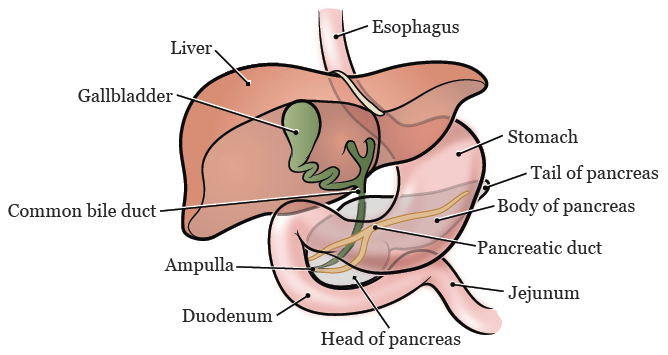
- Your pancreas makes enzymes that help digest the food you eat, including fats. It also makes insulin and glucagon, which are hormones that help regulate your blood sugar levels. Your pancreas has 3 parts: the tail, the body, and the head. The head of your pancreas is attached to your duodenum.
- Your gallbladder stores bile. Bile is a liquid that’s made in your liver that helps digest fats. When you eat food, your gallbladder sends stored bile to your duodenum to help with digestion.
- Your common bile duct is a small tube that carries bile from your liver to your gallbladder to be stored, then from your gallbladder to your duodenum when you eat.
- Your ampulla (also called the ampulla of Vater) is a small sac where your common bile duct and your pancreatic duct meet. It’s located outside your duodenum, near the head of your pancreas.
- Your duodenum is the first part of your small intestine. It’s directly attached to your stomach.
- Your jejunum is the second part of your small intestine.
Even though part of your pancreas will be removed during your surgery, there’s usually enough of it left after your surgery to make hormones (insulin and glucagon) and digestive enzymes.
- If your pancreas doesn’t make enough digestive enzymes after your surgery, you may have diarrhea. If this happens, you may need to take enzyme pills when you eat.
- If your pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin after your surgery, you may have high blood sugar. This is rare. If you do have high blood sugar after your surgery, your healthcare team will help you.
About the Whipple procedure
The Whipple procedure is done using one large incision (surgical cut) in your abdomen. Sometimes, before making the large incision, your surgeon will make several small incisions and put a small video camera into your abdomen. They will use the camera to look at your organs to see if the cancer has spread outside of your pancreas. This is called a diagnostic laparoscopy.
If the cancer has spread, your surgeon may decide not to continue with your surgery. If the cancer hasn’t spread, your surgeon will make a large incision and continue with the Whipple procedure to try to remove the tumor.
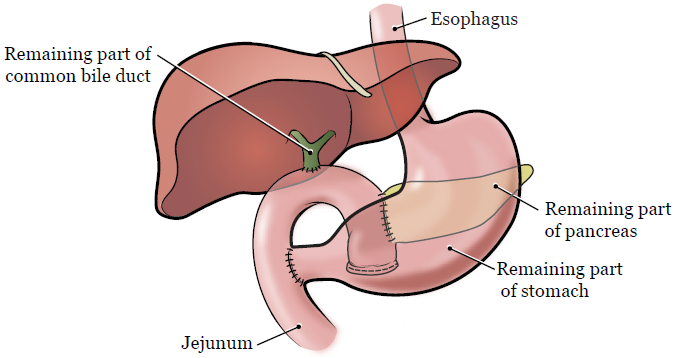
During your surgery, your surgeon will remove the head of your pancreas, your duodenum, the end of your common bile duct closest to your duodenum, and your gallbladder. Sometimes, part of your stomach must also be removed.
After these organs are removed, your surgeon will connect the rest of your common bile duct and your remaining pancreas to your jejunum (see Figure 2). This is so the pancreatic enzymes and bile will flow into your small intestine, like they did before your surgery.
Your surgery will take about 4 hours.
Before your Whipple procedure
This section will help you get ready for your surgery. Read it when your surgery is scheduled. Refer to it as your surgery gets closer. It has important information about what to do to get ready.
As you read this section, write down questions to ask your healthcare provider.
Getting ready for your surgery
You and your care team will work together to get ready for your surgery. Help us keep you safe by telling us if any of these things apply to you, even if you’re not sure.
You may need to follow special instructions before surgery based on the medicines and supplements you take. If you do not follow those instructions, your surgery may be delayed or canceled.
-
I take any prescription medicines. A prescription medicine is one you can only get with a prescription from a healthcare provider. Examples include:
- Medicines you swallow.
- Medicines you take as an injection (shot).
- Medicines you inhale (breathe in).
- Medicines you put on your skin as a patch or cream.
- I take any over-the-counter medicines, including patches and creams. An over-the-counter medicine is one you can buy without a prescription.
- I take any dietary supplements, such as herbs, vitamins, minerals, or natural or home remedies.
- I have a pacemaker, automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD), or other heart device.
- I have had a problem with anesthesia (A-nes-THEE-zhuh) in the past. Anesthesia is medicine to make you sleep during a surgery or procedure.
- I’m allergic to certain medicines or materials, including latex.
- I’m not willing to receive a blood transfusion.
- I use recreational drugs, such as marijuana.
About drinking alcohol
It’s important to talk with your healthcare providers about how much alcohol you drink. This will help us plan your care.
If you drink alcohol regularly, you may be at risk for problems during and after your surgery. These include bleeding, infections, heart problems, and a longer hospital stay.
If you drink alcohol regularly and stop suddenly, it can cause seizures, delirium, and death. If we know you’re at risk for these problems, we can prescribe medicine to help prevent them.
Here are things you can do before your surgery to keep from having problems.
- Be honest with your healthcare providers about how much alcohol you drink.
-
Try to stop drinking alcohol once your surgery is planned. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you:
- Get a headache.
- Feel nauseous (like you’re going to throw up).
- Feel more anxious (nervous or worried) than usual.
- Cannot sleep.
These are early signs of alcohol withdrawal and can be treated.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you cannot stop drinking.
- Ask your healthcare provider questions about drinking and surgery. All your medical information will be kept private, as always.
About smoking
If you smoke or use an electronic smoking device, you can have breathing problems when you have surgery. Vapes and e-cigarettes are examples of electronic smoking devices. Stopping for even a few days before surgery can help prevent breathing problems during and after surgery.
Your healthcare provider will refer you to our Tobacco Treatment Program if you smoke. You can also reach the program by calling 212-610-0507.
About sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a common breathing problem. If you have sleep apnea, you stop breathing for short lengths of time while you’re asleep. The most common type is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). With OSA, your airway becomes fully blocked during sleep.
OSA can cause serious problems during and after surgery. Tell us if you have or think you might have sleep apnea. If you use a breathing device, such as a CPAP machine, bring it on the day of your surgery.
Using MSK MyChart
MSK MyChart (mskmychart.mskcc.org) is MSK’s patient portal. You can use it to send and read messages from your care team, view your test results, see your appointment dates and times, and more. You can also invite your caregiver to make their own account so they can see information about your care.
If you do not have an MSK MyChart account, you can sign up at mskmychart.mskcc.org. You can also ask a member of your care team to send you an invitation.
If you need help with your account, call the MSK MyChart Help Desk at 646-227-2593. They are available Monday through Friday between and (Eastern time).
About Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS)
ERAS is a program to help you get better faster after your surgery. It’s important to do certain things before and after your surgery as part of the ERAS program.
Before your surgery, make sure you’re ready by:
- Reading this guide. It will help you know what to expect before, during, and after your surgery. If you have questions, write them down. You can ask your healthcare provider at your next visit or call their office.
- Exercising and following a healthy diet. This will help get your body ready for your surgery.
After your surgery, help yourself recover more quickly by:
- Reading your recovery pathway. This is an educational resource your healthcare provider will give you. It has goals for your recovery. It will help you know what to do and expect each day.
- Starting to move around as soon as you can. The sooner you get out of bed and walk, the quicker you can get back to your usual activities.
Within 30 days of your surgery
Presurgical testing (PST)
You’ll have a PST appointment before your surgery. You’ll get a reminder from your surgeon’s office with the appointment date, time, and location. Visit www.msk.org/parking for parking information and directions to all MSK locations.
You can eat and take your usual medicines the day of your PST appointment.
It’s helpful to bring these things to your appointment:
- A list of all the medicines you’re taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, patches, and creams.
- Results of any medical tests done outside of MSK in the past year, if you have them. Examples include results from a cardiac stress test, echocardiogram, or carotid doppler study.
- The names and telephone numbers of your healthcare providers.
You’ll meet with an advance practice provider (APP) during your PST appointment. They work closely with MSK’s anesthesiology (A-nes-THEE-zee-AH-loh-jee) staff. These are doctors with special training in using anesthesia during a surgery or procedure.
Your APP will review your medical and surgical history with you. You may have tests to plan your care, such as:
- An electrocardiogram (EKG) to check your heart rhythm.
- A chest X-ray.
- Blood tests.
Your APP may recommend you see other healthcare providers. They’ll also talk with you about which medicine(s) to take the morning of your surgery.
Identify your caregiver
Your caregiver has an important role in your care. Before your surgery, you and your caregiver will learn about your surgery from your healthcare providers. After your surgery, your caregiver will take you home when you’re discharged. They’ll also help you care for yourself at home.
For caregivers
Caring for a person going through cancer treatment comes with many responsibilities. We offer resources and support to help you manage them. Visit www.msk.org/caregivers or read A Guide for Caregivers to learn more.
Fill out a Health Care Proxy form
If you have not already filled out a Health Care Proxy form, we recommend you do now. If you already filled one out or have any other advance directives, bring them to your next appointment.
A health care proxy is a legal document. It says who will speak for you if you cannot communicate for yourself. This person is called your health care agent.
- To learn about health care proxies and other advance directives, read Advance Care Planning for People With Cancer and Their Loved Ones.
- To learn about being a health care agent, read How to Be a Health Care Agent.
Talk with a member of your care team if you have questions about filling out a Health Care Proxy form.
Do breathing and coughing exercises
Practice taking deep breaths and coughing before your surgery. Your healthcare provider will give you an incentive spirometer to help expand your lungs. To learn more, read How To Use Your Incentive Spirometer.
Do physical activity
Doing physical activity will help your body get into its best condition for your surgery. It will also make your recovery faster and easier.
Try to do physical activity every day. Any activity that makes your heart beat faster, such as walking, swimming, or biking, is a good choice. If it’s cold outside, use stairs in your home or go to a mall or shopping center.
Follow a healthy diet
Follow a well-balanced, healthy diet before your surgery. If you need help with your diet, talk with your healthcare provider about meeting with a clinical dietitian nutritionist.
7 days before your surgery
Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for taking aspirin
Aspirin can cause bleeding. If you take aspirin or a medicine that has aspirin, you may need to change your dose or stop taking it 7 days before your surgery. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions. Do not stop taking aspirin unless they tell you to.
To learn more, read How To Check if a Medicine or Supplement Has Aspirin, Other NSAIDs, Vitamin E, or Fish Oil.
Stop taking vitamin E, multivitamins, herbal remedies, and other dietary supplements
Vitamin E, multivitamins, herbal remedies, and other dietary supplements can cause bleeding. Stop taking them 7 days before your surgery. If your healthcare provider gives you other instructions, follow those instead.
To learn more, read Herbal Remedies and Cancer Treatment.
2 days before your surgery
Stop taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen (Advil® and Motrin®) and naproxen (Aleve®), can cause bleeding. Stop taking them 2 days before your surgery. If your healthcare provider gives you other instructions, follow those instead.
To learn more, read How To Check if a Medicine or Supplement Has Aspirin, Other NSAIDs, Vitamin E, or Fish Oil.
1 day before your surgery
Note the time of your surgery
A staff member will call you after the day before your surgery. If your surgery is scheduled for a Monday, they’ll call you the Friday before. If you do not get a call by , call 212-639-5014.
The staff member will tell you what time to get to the hospital for your surgery. They’ll also remind you where to go.
This will be the following location:
Presurgical Center (PSC) on the 6th floor
1275 York Ave. (between East 67th and East 68th streets)
New York, NY 10065
Take the B elevator to the 6th floor.
Visit www.msk.org/parking for parking information and directions to all MSK locations.
Shower with a 4% chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) solution antiseptic skin cleanser (such as Hibiclens®)
4% CHG solution is a skin cleanser that kills germs for 24 hours after you use it. Showering with it before your surgery will help lower your risk of infection after surgery. Your nurse will give you a bottle to use before your surgery.
The night before your surgery, shower using a 4% CHG solution antiseptic skin cleanser.
- Wash your hair with your usual shampoo and conditioner. Rinse your head well.
- Wash your face and genital (groin) area with your usual soap. Rinse your body well with warm water.
- Open the 4% CHG solution bottle. Pour some into your hand or a clean washcloth.
- Move away from the shower stream. Rub the 4% CHG solution gently over your body from your neck to your feet. Do not put it on your face or genital area.
- Move back into the shower stream to rinse off the 4% CHG solution. Use warm water.
- Dry yourself off with a clean towel.
Do not put on any lotion, cream, deodorant, makeup, powder, perfume, or cologne after your shower.
Instructions for eating
Stop eating at midnight (12 a.m.) the night before your procedure. This includes hard candy and gum.
Your healthcare provider may have given you different instructions for when to stop eating. If so, follow their instructions. Some people need to fast (not eat) for longer before their procedure.
The day of your surgery
Instructions for drinking
Between midnight (12 a.m.) and 2 hours before your arrival time, only drink the liquids on the list below. Do not eat or drink anything else. Stop drinking 2 hours before your arrival time.
- Water.
- Clear apple juice, clear grape juice, or clear cranberry juice.
- Gatorade or Powerade.
-
Black coffee or plain tea. It’s OK to add sugar. Do not add anything else.
- Do not add any amount of any type of milk or creamer. This includes plant-based milks and creamers.
- Do not add honey.
- Do not add flavored syrup.
If you have diabetes, pay attention to the amount of sugar in your drinks. It will be easier to control your blood sugar levels if you include sugar-free, low-sugar, or no added sugar versions of these drinks.
It’s helpful to stay hydrated before surgery, so drink if you are thirsty. Do not drink more than you need. You will get intravenous (IV) fluids during your surgery.
Stop drinking 2 hours before your arrival time. This includes water.
Your healthcare provider may have given you different instructions for when to stop drinking. If so, follow their instructions.
Take your medicines as instructed
A member of your care team will tell you which medicines to take the morning of your surgery. Take only those medicines with a sip of water. Depending on what you usually take, this may be all, some, or none of your usual morning medicines.
Shower with a 4% CHG solution antiseptic skin cleanser, such as Hibiclens
Shower with a 4% CHG solution antiseptic skin cleanser before you leave for the hospital. Use it the same way you did the night before.
Do not put on any lotion, cream, deodorant, makeup, powder, perfume, or cologne after your shower.
Things to remember
- Wear something comfortable and loose-fitting.
- If you wear contact lenses, wear your glasses instead. Wearing contact lenses during surgery can damage your eyes.
- Do not wear any metal objects. Take off all jewelry, including body piercings. The tools used during your surgery can cause burns if they touch metal.
- Leave valuable items at home.
- If you’re menstruating (have your monthly period), use a sanitary pad, not a tampon. We’ll give you disposable underwear and a pad if you need them.
What to bring
- Sneakers that lace up. You may have some swelling in your feet after surgery. Lace-up sneakers can fit over this swelling.
- Your breathing device for sleep apnea (such as your CPAP machine), if you have one.
- Your Health Care Proxy form and other advance directives, if you filled them out.
- Your cell phone and charger.
- Only the money you may want for small purchases, such as a newspaper.
- A case for your personal items, if you have any. Eyeglasses, hearing aids, dentures, prosthetic devices, wigs, and religious articles are examples of personal items.
- This guide. You’ll use it to learn how to care for yourself after surgery.
Once you’re in the hospital
When you get to the hospital, take the B elevator to the 6th floor. Check in at the desk in the PSC waiting room.
Many staff members will ask you to say and spell your name and birth date. This is for your safety. People with the same or a similar name may be having surgery on the same day.
We’ll give you a hospital gown, robe, and nonskid socks to wear when it’s time to change for surgery.
For caregivers, family, and friends
Read Information for Family and Friends for the Day of Surgery to help you know what to expect on the day of your loved one’s surgery.
Meet with a nurse
You’ll meet with a nurse before surgery. Tell them the dose of any medicines you took after midnight (12 a.m.) and the time you took them. Make sure to include prescription and over-the-counter medicines, patches, and creams.
Your nurse may give you medication to help with pain after surgery. If they do, they will give you information about the medication before you take it.
Your nurse may also place an intravenous (IV) line in one of your veins, usually in your arm or hand. If your nurse does not place the IV, your anesthesiologist (A-nes-THEE-zee-AH-loh-jist) will do it in the operating room.
Meet with an anesthesiologist
You’ll also meet with an anesthesiologist before surgery. They will:
- Review your medical history with you.
- Ask if you’ve had any problems with anesthesia in the past. This includes nausea (feeling like you’re going to throw up) or pain.
- Talk with you about your comfort and safety during your surgery.
- Talk with you about the kind of anesthesia you’ll get.
- Answer questions you have about anesthesia.
Your doctor or anesthesiologist may also talk with you about placing an epidural catheter (thin, flexible tube) in your spine (back). An epidural catheter is another way to give you pain medication after your surgery.
Get ready for surgery
When it’s time for your surgery, you’ll take off your eyeglasses, hearing aids, dentures, prosthetic devices, wig, and religious articles.
You’ll either walk into the operating room or a staff member will bring you there on a stretcher. A member of the operating room team will help you onto the operating bed. They’ll put compression boots on your lower legs. These gently inflate and deflate to help blood flow in your legs.
Once you’re comfortable, your anesthesiologist will give you anesthesia through your IV line and you’ll fall asleep. You’ll also get fluids through your IV line during and after your surgery.
During your surgery
After you’re fully asleep, your care team will place a breathing tube through your mouth into your airway. It will help you breathe. They’ll also place a urinary (Foley) catheter in your bladder. It will drain your urine (pee) during your surgery.
Your surgeon will close your incisions with staples or stitches once they finish your surgery. They may also place Steri-Strips™ (thin pieces of surgical tape) over your incisions. They’ll cover your incisions with a bandage.
Your care team will usually take out your breathing tube while you’re still in the operating room.
After your Whipple procedure
This section will help you know what to expect after your surgery. You’ll learn how to safely recover from your surgery both in the hospital and at home.
As you read this section, write down questions to ask your healthcare provider.
In the Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU)
You’ll be in the PACU when you wake up after your surgery. A nurse will be keeping track of your temperature, pulse, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. You may get oxygen through a tube resting below your nose or a mask over your nose and mouth. You’ll also have compression boots on your lower legs.
Pain medication
You’ll get epidural or IV pain medication while you’re in the PACU.
- If you’re getting epidural pain medication, it will be put into your epidural space (the space in your spine just outside your spinal cord) through your epidural catheter.
- If you’re getting IV pain medication, it will be put into your bloodstream through your IV line.
You’ll be able to control your pain medication using a button called a patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) device. To learn more, read Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA).
Tubes and drains
You will have 1 or more of the tubes and drains below. Your doctor or nurse will talk with you about what to expect.
- You will have a Foley catheter in your urethra going into your bladder. This tube drains urine from your bladder so your care team can keep track of how much urine you’re making. Your Foley catheter is usually removed 2 days after your surgery.
- You may have a nasogastric (NG) tube in your nose going into your stomach. This tube drains the fluid that naturally collects in your stomach. It will help keep you from vomiting (throwing up). If you have a NG tube, it’s usually removed the first day after surgery.
- You may have a drainage tube in your abdomen to drain fluid from the area. If you have this drainage tube, it’s usually removed a few days after surgery, but you may still have it when you’re discharged from the hospital. Read the “Caring for Your Tubes and Drains” section for more information.
Moving to your hospital room
You’ll stay in the PACU overnight. After your stay in the PACU, a staff member will take you to your hospital room.
In your hospital room
The length of time you’re in the hospital after your surgery depends on your recovery. Most people stay in the hospital for 6 days.
In your hospital room, you’ll meet one of the nurses who will care for you during your stay. A nurse will help you out of bed and into your chair soon after you get there.
Your care team will teach you how to care for yourself while you’re healing from your surgery. You can help yourself recover more quickly by:
- Reading your recovery pathway. We will give you a pathway with goals for your recovery if you do not already have one. It will help you know what to do and expect on each day during your recovery.
- Starting to move around as soon as you can. The sooner you get out of bed and walk, the quicker you can get back to your usual activities.
Read Call! Don't Fall! to learn what you can do to stay safe and keep from falling while you’re in the hospital.
Managing your pain
You’ll have some pain after your surgery. At first, you’ll get your pain medicine through your epidural catheter or IV line. You’ll be able to control your pain medicine using a PCA device. Once you can eat, you’ll get oral pain medicine (pain medicine you swallow).
We will ask you about your pain often and give you medicine as needed. Tell one of your healthcare providers if your pain is not relieved. It’s important to control your pain so you can use your incentive spirometer and move around. Controlling your pain can help you recover faster.
You’ll get a prescription for pain medicine before you leave the hospital. Talk with your healthcare provider about possible side effects. Ask them when to start switching to over-the-counter pain medicine.
Moving around and walking
Moving around and walking will help lower your risk for blood clots and pneumonia (lung infection). It will also help you start passing gas and having bowel movements (pooping) again. Your nurse, physical therapist, or occupational therapist will help you move around, if needed.
To learn more about how walking can help you recover, read Frequently Asked Questions About Walking After Your Surgery.
To learn what you can do to stay safe and keep from falling while you’re in the hospital, read Call! Don't Fall!.
Exercising your lungs
It’s important to exercise your lungs so they expand fully. This helps prevent pneumonia.
- Use your incentive spirometer 10 times every hour you’re awake. Read How To Use Your Incentive Spirometer to learn more.
- Do coughing and deep breathing exercises. A member of your care team will teach you how.
Eating and drinking
During your surgery, some of your digestive organs were moved or removed. After your surgery, your digestive system needs time to heal and adjust to the changes. You will slowly go back to drinking and eating. The table below is a guideline. Follow your healthcare team’s instructions.
| Days after surgery | Diet |
|---|---|
| The day of surgery | Do not eat or drink anything. |
| 1 day after surgery | Start drinking sips of clear liquids. |
| 2 days after surgery | Follow a clear liquid diet. |
| 3 days after surgery | Start eating small amounts of solid foods. |
| 4 days after surgery | Eat solid foods. |
| 5 days after surgery | Eat solid foods. |
| 6 days after surgery | Eat solid foods. |
An inpatient clinical dietitian nutritionist will visit you in your hospital room to plan your diet with you before you’re discharged.
To learn more about your diet and nutrition after your Whipple procedure, read Diet and Nutrition After Your Whipple Procedure.
Caring for your tubes and drains
Your nurse will help you care for your tubes and drains while you’re in the hospital.
If you have a drainage tube in your abdomen, your healthcare team will keep track of how much fluid is draining from the tube. Once the amount is low enough, they will remove the tube. This usually happens a few days after surgery, but you may still have the drainage tube when you’re discharged from the hospital. Your healthcare team will tell you what to expect.
If you will still have the drainage tube when you’re discharged, your nurse will teach you how to care for it at home. They will also give you the supplies you will need. Your case manager may also arrange for a home care nurse to visit you at home to help you.
Showering
You will be able to shower on the first day after your surgery. A member of your care team will help you.
Leaving the hospital
By the time you’re ready to leave the hospital, your incision will have started to heal. Before you leave, look at your incision with one of your healthcare providers. Knowing what it looks like will help you notice any changes later.
On the day of your discharge, plan to leave the hospital around Your healthcare provider will write your discharge order and prescriptions before you leave. You’ll also get written discharge instructions. One of your healthcare providers will review them with you before you leave.
If your ride isn’t at the hospital when you’re ready to leave, you may be able to wait in the Patient Transition Lounge. A member of your care team will give you more information.
At home
Read What You Can Do to Avoid Falling to learn what you can do to keep from falling at home and during your appointments at MSK.
Your first appointment after surgery will be 10 to 14 days after you leave the hospital. Your nurse will give you instructions on how to make this appointment, including the phone number to call.
Filling out your Recovery Tracker
We want to know how you’re feeling after you leave the hospital. To help us care for you, we’ll send questions to your MSK MyChart account. We’ll send them every day for 10 days after you’re discharged. These questions are known as your Recovery Tracker.
Fill out your Recovery Tracker every day before midnight (12 a.m.). It only takes 2 to 3 minutes to complete. Your answers to these questions will help us understand how you’re feeling and what you need.
Based on your answers, we may reach out to you for more information. Sometimes, we may ask you to call your surgeon’s office. You can always contact your surgeon’s office if you have any questions.
To learn more, read Common Questions About MSK's Recovery Tracker.
Managing your pain
People have pain or discomfort for different lengths of time. You may still have some pain when you go home and will probably be taking pain medicine. Some people have soreness, tightness, or muscle aches around their incision as they recover. This doesn’t mean something is wrong.
Follow these guidelines to help manage your pain at home.
- Take your medicines as directed and as needed.
- Call your healthcare provider if the medicine prescribed for you does not help your pain.
- Do not drive or drink alcohol while you’re taking prescription pain medicine. Some prescription pain medicines can make you drowsy (very sleepy). Alcohol can make the drowsiness worse.
-
You’ll have less pain and need less pain medicine as your incision heals. An over-the-counter pain reliever will help with aches and discomfort. Acetaminophen (Tylenol®) and ibuprofen (Advil or Motrin) are examples of over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for stopping your prescription pain medicine.
- Do not take too much of any medicine. Follow the instructions on the label or from your healthcare provider.
- Read the labels on all the medicines you’re taking. This is very important if you’re taking acetaminophen. Acetaminophen is an ingredient in many over-the-counter and prescription medicines. Taking too much can harm your liver. Do not take more than one medicine that has acetaminophen without talking with a member of your care team.
- Pain medicine should help you get back to your usual activities. Take enough to do your activities and exercises comfortably. You may have a little more pain as you start to be more active.
- Keep track of when you take your pain medicine. It works best 30 to 45 minutes after you take it. Taking it when you first have pain is better than waiting for the pain to get worse.
Some prescription pain medicines, such as opioids, may cause constipation. Constipation is when you poop less often than usual, have a harder time pooping, or both.
Preventing and managing constipation
Talk with your healthcare provider about how to prevent and manage constipation. You can also follow the guidelines below.
- Go to the bathroom at the same time every day. Your body will get used to going at that time. But if you feel like you need to go, don’t put it off.
- Exercise, if you can. Walking is a great type of exercise that can help prevent and manage constipation.
- Drink around 8 (8-ounce) cups(2 liters) of liquids daily, if you can. Follow the instructions in Diet and Nutrition After Your Whipple Procedure.
If you haven’t had a bowel movement in 2 days, call your healthcare provider.
Managing diarrhea
If your pancreas doesn’t make enough enzymes to digest your food, you may have diarrhea. If this happens, contact your doctor’s office. You may need to take enzyme pills when you eat. Your doctor or nurse will give you more information.
Caring for your incision
It’s normal for the skin below your incision to feel numb. This happens because some of your nerves were cut during your surgery. The numbness will go away over time.
The staples in your incision will be removed during your first appointment after surgery. This is usually about 2 weeks after you’re discharged. While the staples are in your incision, you may feel some tightness or a tugging feeling along your incision. This is normal. Doing gentle stretching can help.
If you go home with Steri-Strips on your incision, they will loosen and fall off by themselves. If they haven’t fallen off within 10 days, you can take them off.
If the area around your incision is red, puffy, or if you have any drainage from your incision, contact your doctor’s office.
Showering
Shower every day. Taking a warm shower is relaxing and can help ease muscle aches. You will also clean your incision when you shower.
When you shower, use soap to gently wash your incision. After you shower, pat the area dry with a clean towel. Don’t rub over your incision. Leave your incision uncovered, unless there’s drainage.
Don’t take tub baths until you discuss it with your doctor at your first appointment after your surgery.
Eating and drinking
After your surgery, you may have a smaller appetite (desire to eat) or no appetite at all. You will probably feel full quickly after eating. These are expected and should get better over time.
If you find your appetite isn’t good at first, try having meals that include your favorite foods and high-calorie foods. It’s important to get enough calories and protein to promote healing keep from losing weight. You should think of food as being as important as your medications.
Follow the eating and drinking guidelines in msk-node-link: 20275]. If you have questions, you can reach a clinical dietitian nutritionist by calling 212-639-7312.
Weight changes
Many people lose weight after their surgery. You may not get back to your pre-surgery weight for some time. Your goal should be to stay at your new weight. If you have questions or concerns about your weight, talk with a member of your healthcare team.
Physical activity and exercise
When you leave the hospital, your incision will look like it’s healed on the outside, but it won’t be healed on the inside.
- Don’t lift anything heavier than 5 pounds (2.3 kilograms) for at least 8 weeks after your surgery. Check with your doctor before you do any heavy lifting.
- Ask your doctor or nurse before starting strenuous exercises, such as jogging and tennis.
Doing aerobic exercise, such as walking and stair climbing, will help you gain strength and feel better. You can walk outside or indoors at your local mall or shopping center. Gradually increase the distance you walk. Climb stairs slowly, resting or stopping as needed. You can also keep doing your coughing and deep breathing exercises and using your incentive spirometer.
Managing fatigue
Fatigue is having less energy or feeling more tired than usual. It’s normal to feel fatigued after your surgery. This may last for 6 to 8 weeks after surgery, but it will get better slowly over time. Try to increase your activity level every day to help manage your fatigue. Get up, get dressed, and walk. You may need a nap during the day, but try to stay out of bed as much as possible so you will sleep at night.
It’s important for you to go back to your usual activities after surgery. Spread them out over the course of the day. You can do light household tasks. Try washing dishes, preparing light meals, and other activities as you are able.
Your body is an excellent guide for telling you when you have done too much. When you increase your activity, monitor your body’s reaction. You may find that you have more energy in the morning or the afternoon. Plan your activities for times of the day when you have more energy.
Driving
While your incision is healing, you may not be able to twist your body as well as normal. This can make it hard for you to drive. You also shouldn’t drive if you’re taking pain medication that may make you drowsy. During your first appointment after surgery, your doctor will tell you if it’s safe for you to start driving again.
You can ride in a car as a passenger at any time after you leave the hospital.
Going back to work
Talk with your healthcare provider about your job. They’ll tell you when it may be safe for you to start working again based on what you do. If you move around a lot or lift heavy objects, you may need to stay out a little longer. If you sit at a desk, you may be able to go back sooner.
Traveling
If you’re traveling a long distance, try to get up once an hour to walk around. This will help prevent blood clots. Remember to drink around 8 (8-ounce) cups of liquids every day, even when you’re traveling.
Managing your feelings
You may have new and upsetting feelings after a surgery for a serious illness. Many people say they felt weepy, sad, worried, nervous, irritable, or angry at one time or another. You may find that you cannot control some of these feelings. If this happens, it’s a good idea to seek emotional support. Your healthcare provider can refer you to MSK’s Counseling Center. You can also reach them by calling 646-888-0200.
The first step in coping is to talk about how you feel. Family and friends can help. We can also reassure, support, and guide you. It’s always a good idea to let us know how you, your family, and your friends are feeling emotionally. Many resources are available to you and your family. We’re here to help you and your family and friends handle the emotional aspects of your illness. We can help no matter if you’re in the hospital or at home.
When to call your healthcare provider
Call your healthcare provider if:
- You have a fever of 100.5 °F (38 °C) or higher.
- You have chills.
- You have shortness of breath.
- The skin around your incision is warmer than normal.
- The skin around your incision is getting more red.
- The area around your incision is starting to swell.
- Swelling around your incision is getting worse.
- You have pus-like (thick, yellowish, or foul-smelling) drainage from your incision.
- You have any sudden increase in pain or new pain.
- You have nausea and vomiting.
- You have diarrhea.
- You have constipation that isn’t relieved within 2 days.
- You have any new or unexplained symptoms.
- You have any questions or concerns.
Monday through Friday from to , contact your healthcare provider.
After , during the weekend, and on holidays, call 212-639-2000 and ask to speak to the person on call for your healthcare provider.
Support services
This section has a list of support services. They may help you as you get ready for your surgery and recover after your surgery.
As you read this section, write down questions to ask your healthcare provider.
MSK support services
Admitting Office
212-639-7606
Call if you have questions about your hospital admission, such as asking for a private room.
Anesthesia
212-639-6840
Call if you have questions about anesthesia.
Blood Donor Room
212-639-7643
Call for information if you’re interested in donating blood or platelets.
Bobst International Center
www.msk.org/international
888-675-7722
We welcome patients from around the world and offer many services to help. If you’re an international patient, call for help arranging your care.
Counseling Center
www.msk.org/counseling
646-888-0200
Many people find that counseling helps them. Our Counseling Center offers counseling for individuals, couples, families, and groups. We can also prescribe medicine to help if you feel anxious or depressed. Ask a member of your care team for a referral or call the number above to make an appointment.
Food Pantry Program
646-888-8055
We give food to people in need during their cancer treatment. Talk with a member of your care team or call the number above to learn more.
Integrative Medicine and Wellness Service
www.msk.org/integrativemedicine
Our Integrative Medicine and Wellness Service offers many services to complement (go along with) traditional medical care. For example, we offer music therapy, mind/body therapies, dance and movement therapy, yoga, and touch therapy. Call 646-449-1010 to make an appointment for these services.
You can also schedule a consultation with a healthcare provider in the Integrative Medicine and Wellness Service. They’ll work with you to make a plan for creating a healthy lifestyle and managing side effects. Call 646-608-8550 to make an appointment for a consultation.
MSK Library
library.mskcc.org
You can visit our library website or email [email protected] to talk with the library reference staff. They can help you find more information about a type of cancer. You can also visit the library’s Patient Education Resource Guide.
Nutrition Services
www.msk.org/nutrition
212-639-7312
Our Nutrition Service offers nutritional counseling with one of our clinical dietitian nutritionists. Your clinical dietitian nutritionist will talk with you about your eating habits. They can also give advice on what to eat during and after treatment. Ask a member of your care team for a referral or call the number above to make an appointment.
Patient and Community Education
www.msk.org/pe
Visit our patient and community education website to search for educational resources, videos, and online programs.
Patient Billing
646-227-3378
Call if you have questions about preauthorization with your insurance company. This is also called preapproval.
Patient Representative Office
212-639-7202
Call if you have questions about the Health Care Proxy form or concerns about your care.
Perioperative Nurse Liaison
212-639-5935
Call if you have questions about MSK releasing any information while you’re having surgery.
Private Duty Nurses and Companions
646-357-9272
You can request private nurses or companions to care for you in the hospital and at home. Call to learn more.
Rehabilitation Services
www.msk.org/rehabilitation
Cancers and cancer treatments can make your body feel weak, stiff, or tight. Some can cause lymphedema (swelling). Our physiatrists (rehabilitation medicine doctors), occupational therapists (OTs), and physical therapists (PTs) can help you get back to your usual activities.
- Rehabilitation medicine doctors diagnose and treat problems that affect how you move and do activities. They can design and help coordinate your rehabilitation therapy program, either at MSK or somewhere closer to home. Call Rehabilitation Medicine (Physiatry) at 646-888-1929 to learn more.
- An OT can help if you’re having trouble doing usual daily activities. For example, they can recommend tools to help make daily tasks easier. A PT can teach you exercises to help build strength and flexibility. Call Rehabilitation Therapy at 646-888-1900 to learn more.
Resources for Life After Cancer (RLAC) Program
646-888-8106
At MSK, care does not end after your treatment. The RLAC Program is for patients and their families who have finished treatment.
This program has many services. We offer seminars, workshops, support groups, and counseling on life after treatment. We can also help with insurance and employment issues.
Sexual Health Programs
Cancer and cancer treatments can affect your sexual health, fertility, or both. MSK’s sexual health programs can help you before, during, or after your treatment.
- Our Female Sexual Medicine and Women’s Health Program can help with sexual health problems such as premature menopause or fertility issues. Ask a member of your MSK care team for a referral or call 646-888-5076 to learn more.
- Our Male Sexual and Reproductive Medicine Program can help with sexual health problems such as erectile dysfunction (ED). Ask a member of your care team for a referral or call 646-888-6024 to learn more.
Social Work
www.msk.org/socialwork
212-639-7020
Social workers help patients, families, and friends deal with common issues for people who have cancer. They provide individual counseling and support groups throughout your treatment. They can help you communicate with children and other family members.
Our social workers can also help refer you to community agencies and programs. If you’re having trouble paying your bills, they also have information about financial resources. Call the number above to learn more.
Spiritual Care
212-639-5982
Our chaplains (spiritual counselors) are available to listen, help support family members, and pray. They can contact community clergy or faith groups, or simply be a comforting companion and a spiritual presence. Anyone can ask for spiritual support. You do not have to have a religious affiliation (connection to a religion).
MSK’s interfaith chapel is located near Memorial Hospital’s main lobby. It’s open 24 hours a day. If you have an emergency, call 212-639-2000. Ask for the chaplain on call.
Tobacco Treatment Program
www.msk.org/tobacco
212-610-0507
If you want to quit smoking, MSK has specialists who can help. Call to learn more.
Virtual Programs
www.msk.org/vp
We offer online education and support for patients and caregivers. These are live sessions where you can talk or just listen. You can learn about your diagnosis, what to expect during treatment, and how to prepare for your cancer care.
Sessions are private, free, and led by experts. Visit our website to learn more about Virtual Programs or to register.
External support services
Access-A-Ride
web.mta.info/nyct/paratran/guide.htm
877-337-2017
In New York City, the MTA offers a shared ride, door-to-door service for people with disabilities who can’t take the public bus or subway.
Air Charity Network
www.aircharitynetwork.org
877-621-7177
Provides travel to treatment centers.
American Cancer Society (ACS)
www.cancer.org
800-ACS-2345 (800-227-2345)
Offers a variety of information and services, including Hope Lodge, a free place for patients and caregivers to stay during cancer treatment.
Cancer and Careers
www.cancerandcareers.org
646-929-8032
A resource for education, tools, and events for employees with cancer.
CancerCare
www.cancercare.org
800-813-4673
275 Seventh Avenue (Between West 25th & 26th Streets)
New York, NY 10001
Provides counseling, support groups, educational workshops, publications, and financial assistance.
Cancer Support Community
www.cancersupportcommunity.org
Provides support and education to people affected by cancer.
Caregiver Action Network
www.caregiveraction.org
800-896-3650
Provides education and support for people who care for loved ones with a chronic illness or disability.
Corporate Angel Network
www.corpangelnetwork.org
866-328-1313
Offers free travel to treatment across the country using empty seats on corporate jets.
Good Days
www.mygooddays.org
877-968-7233
Offers financial assistance to pay for copayments during treatment. Patients must have medical insurance, meet the income criteria, and be prescribed medicine that’s part of the Good Days formulary.
HealthWell Foundation
www.healthwellfoundation.org
800-675-8416
Provides financial assistance to cover copayments, health care premiums, and deductibles for certain medicines and therapies.
Joe’s House
www.joeshouse.org
877-563-7468
Provides a list of places to stay near treatment centers for people with cancer and their families.
LGBT Cancer Project
www.lgbtcancer.com
Provides support and advocacy for the LGBT community, including online support groups and a database of LGBT-friendly clinical trials.
LIVESTRONG Fertility
www.livestrong.org/fertility
855-744-7777
Provides reproductive information and support to cancer patients and survivors whose medical treatments have risks associated with infertility.
Look Good Feel Better Program
www.lookgoodfeelbetter.org
800-395-LOOK (800-395-5665)
This program offers workshops to learn things you can do to help you feel better about your appearance. For more information or to sign up for a workshop, call the number above or visit the program’s website.
National Cancer Institute
www.cancer.gov
800-4-CANCER (800-422-6237)
National Council on Aging (NCOA)
www.benefitscheckup.org
Provides information and resources for older adults. Offers BenefitsCheckUp®, a free online tool that connects you to prescription assistance programs, including Medicare’s Extra Help program.
National LGBT Cancer Network
www.cancer-network.org
Provides education, training, and advocacy for LGBT cancer survivors and those at risk.
Needy Meds
www.needymeds.org
Lists Patient Assistance Programs for brand and generic name medicines.
NYRx
www.health.ny.gov/health_care/medicaid/program/pharmacy.htm
Provides prescription benefits to eligible employees and retirees of public sector employers in New York State.
Patient Access Network (PAN) Foundation
www.panfoundation.org
866-316-7263
Gives help with copayments for patients with insurance.
Patient Advocate Foundation
www.patientadvocate.org
800-532-5274
Provides access to care, financial assistance, insurance assistance, job retention assistance, and access to the national underinsured resource directory.
Red Door Community (formerly known as Gilda’s Club)
www.reddoorcommunity.org
212-647-9700
A place where people living with cancer find social and emotional support through networking, workshops, lectures, and social activities.
RxHope
www.rxhope.com
877-267-0517
Provides assistance to help people get medicines they have trouble affording.
Triage Cancer
www.triagecancer.org
Provides legal, medical, and financial information and resources for cancer patients and their caregivers.
Educational resources
This section lists the educational resources mentioned in this guide. They will help you get ready for your surgery and recover after your surgery.
As you read these resources, write down questions to ask your healthcare provider.
- Advance Care Planning for People With Cancer and Their Loved Ones
- Call! Don't Fall!
- How To Check if a Medicine or Supplement Has Aspirin, Other NSAIDs, Vitamin E, or Fish Oil
- Diet and Nutrition After Your Whipple Procedure
- Herbal Remedies and Cancer Treatment
- How To Use Your Incentive Spirometer
- Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA)
- What You Can Do to Avoid Falling
- Common Questions About MSK's Recovery Tracker
