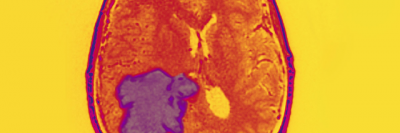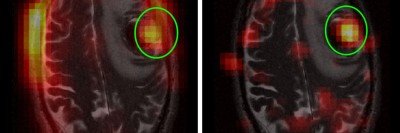
Almost 23,000 American adults and children are diagnosed with a brain or spinal cord tumor each year, according to the American Cancer Society.
There are more than 125 different types of brain cancer, which doctors usually categorize as being either primary — which can be high grade (rapidly growing) or low grade (slow growing) — or metastatic — meaning the cancer began in another part of the body and spread to the brain. You may also hear the terms malignant and benign used. Malignant brain tumors tend to be more rapidly growing and invasive than benign tumors, and are often the life-threatening ones.
Even though a diagnosis of a low-grade tumor may not sound as serious as a high-grade one, these types of brain cancers can also be potentially life-threatening. This is because the skull cannot expand to make room for a growing tumor and it can therefore press on or damage brain tissue. Also, some low-grade brain tumors can behave like, or turn into, high-grade tumors.
There are various risk factors for developing a brain tumor, but contrary to popular belief, there are only two proven environmental risk factors: x-ray exposure to the head and the use of drugs that suppress the immune system.
Symptoms are usually related to the tumor’s location rather than its size. Certain symptoms may also help doctors make a diagnosis as to which kind of brain tumor you have.
Depending on the type of brain tumor you are diagnosed with and the stage of your disease, your doctor may recommend treatment with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or some combination of these. We also offer a number of clinical trials exploring new therapies. Because metastatic brain tumors are made up of different types of cells, treatment differs from that for primary brain tumors.
Available 24 hours a day